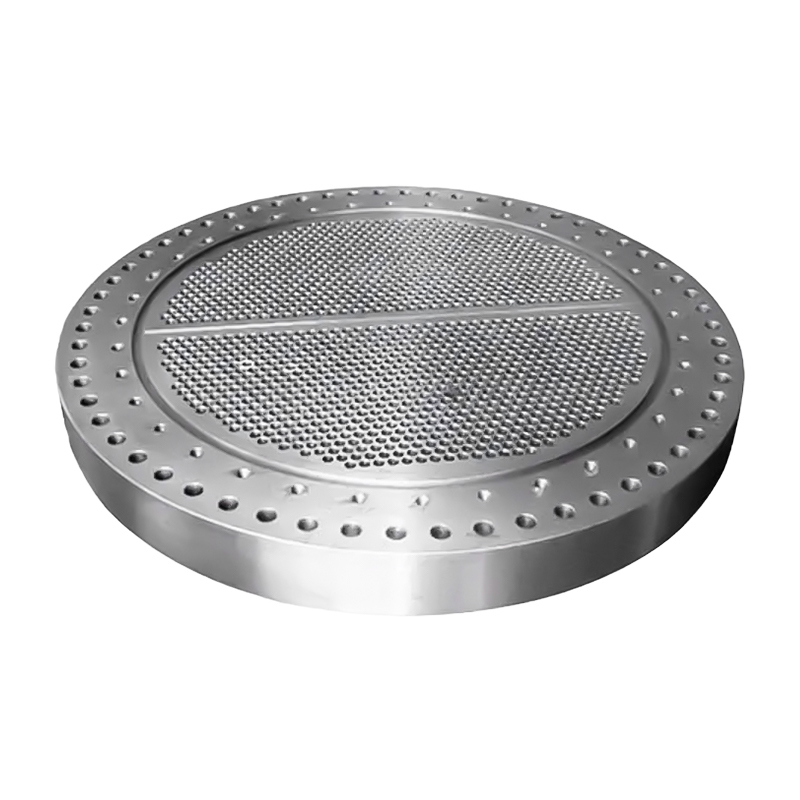
Nuclear Power Forgings Supplier
Nuclear power forgings play a role in supporting and transmitting power in nuclear power equipment. Strict control is implemented throughout the production process to ensure quality. Full-cycle technical support is provided. Their advantages lie in high safety and strong reliability, which guarantee the stable operation of nuclear power facilities.
About Us
ACE Group is a comprehensive enterprise group focused on the heavy industrial manufacturing sector, serving as a China Nuclear Power Forgings Supplier and Nuclear Power Forgings Company. Its business spans forging, heat treatment, precision machining, welded structures, and heavy-duty power & free chain spraying production. This integrated layout covers the core production processes of the industrial machinery industry, combining technological strength with large-scale production capabilities.
Core Subsidiaries Details:
Jiangsu ACE Energy Technology Co., Ltd.: The group's core production base, officially commencing operations in November 2025. It occupies 55 acres with a total floor area exceeding 50,018 square meters. The factory is equipped with 3-ton, 5-ton, and 15-ton electro-hydraulic hammers; 1-meter and 1.5-meter vertical ring rolling machines; energy-efficient natural gas heating furnaces; heat treatment resistance furnaces; quenching tanks; induction hardening equipment; machining centers; and other production equipment.
Yancheng ACE Machinery Co., Ltd.: Established in 2019, it occupies 20 acres with a floor area of 13,333 square meters. It possesses an integrated welding-straightening structural steel production line and a precision machining workshop.
Yancheng ACE Surface Treatment Technology Co., Ltd.: Operates a heavy-duty power & free chain large-scale powder coating production line. Focusing on professional surface treatment technology, One-time coating thickness achieves 400μm, providing reliable anti-corrosion and weather-resistant protective performance and appearance optimization solutions, enhancing the group's full life-cycle product services.
ACE Group is supported by a management team of young key members who are experienced in materials, heat treatment, machining, and surface treatment industries. They are well-versed in international and domestic standards, pioneering, and committed to innovation. The subsidiary ACE Machinery has passed TÜV Rheinland ISO 9001 Quality Management System certification, as well as ISO 14001, 45001, and 50001 system certifications. It is recognised as a Specialised, Refined, Unique, and Innovative Enterprise, a National High-Tech Enterprise, and holds a 3A-level enterprise credit rating.
Relying on integrated MES and ERP management systems, the integration of informatisation and industrialisation, data cloud storage, and aiming to build a modern, energy-efficient enterprise, the group maintains a comprehensive inspection system. It possesses inspection tools, non-destructive testing equipment, and qualified personnel, implementing strict controls from material internal quality to appearance and dimensions. All outgoing products undergo 100% inspection, adhering to the business philosophy of pursuing 100% qualified outgoing products and zero customer complaints. A CNAS-standard laboratory will be established to provide scientific testing support for quality control during production and technological R&D, thereby enhancing product quality and technological innovation.
In the future, ACE Group will continue to leverage the technical advantages and industrial synergies of its subsidiaries. Through standardised production, specialised technology, integrated services, and a stringent quality control system, it is committed to providing efficient and reliable industrial manufacturing solutions for global clients, steadily advancing towards becoming a leading comprehensive manufacturing service provider in the industry.
Certificate
-
Enterprise Credit Evaluation AAA
-
2024 Specialized, Refined, Distinctive, and Innovative Enterprise Certificate
-
2023 High-Tech Enterprise Certificate
-
ISO50001 Energy Management System
-
ISO 45001 Occupational Health and Safety Management System
-
ISO 14001 Environmental Management System
-
ISO 9001 Quality Management System
News
-
Company News 2026-01-25
After 6 months of precision engineering and collaboration, we are proud to announce the completion of our 700m rail supply for the Berendrechtsluis Lock renovation project at the Port of Antwerp-Bruges, Europe's largest integrated port. The final container, carrying 15 pieces of our 34CrNiMo6 QT T-type heavy-duty T-typ...
View More -
News 2026-01-19
On January 17, 2026, the inaugural annual gala of Jiangsu ACE Energy Technology Co., Ltd. was triumphantly held in an atmosphere brimming with enthusiasm. Over 160 attendees, including distinguished guests from various sectors, partners, government representatives, as well as the company's employees and their families,...
View More -
Company News 2025-11-12
With a resounding clang of the hammer, a new journey begins! Recently, the grand opening ceremony of Jiangsu ACE Energy Co., Ltd.'s forging base and the launch ceremony for the "first hammer" production were held in the Dafeng Economic Development Zone Industrial Park, Jiangsu Province. As ACE Energy Chairman Zhai Liuy...
View More
Nuclear Power Forgings KNOWLEDGE
Nuclear power forgings represent the pinnacle of metal manufacturing. These components must remain structural and leak-proof for 60+ years under intense radiation, high pressure, and extreme temperatures. Because safety is paramount, nuclear forgings are governed by the world’s most stringent quality codes, such as ASME Section III.
1. The "Big Three" Heavy Forgings
In a nuclear island, the largest components are often forged as "Integral Rings" to minimize the number of weld seams, which are potential points of failure.
-
Reactor Pressure Vessel (RPV) Shells: The "heart" of the plant. These are massive rings that house the nuclear core. For Gen III+ reactors (like the AP1000 or EPR), these require ingots weighing over 600 tons.
-
Steam Generator Tube Sheets: Massive thick disks that hold thousands of heat exchanger tubes. They must be forged to ensure zero internal porosity.
-
Turbine Rotor Shafts: These transmit power to the generator. They are forged to handle massive rotational inertia and thermal stress without vibrating or cracking.
2. Specialized Materials (The Chemistry of Safety)
Nuclear environments require materials that do not become excessively brittle when pelted by neutrons (a process called neutron embrittlement).
| Material Grade | Key Characteristics | Typical Application |
| SA-508 Grade 3 | Low-alloy steel with high fracture toughness and low impurity levels (P & S). | The primary material for Reactor Pressure Vessels (RPV). |
| SA-336 / F316L | Low-carbon stainless steel; excellent corrosion resistance in borated water. | Primary coolant piping and pump housings. |
| Inconel 600/690 | Nickel-based alloys with extreme heat and corrosion resistance. | Steam generator tubing and internal support structures. |
| SA-533 | Manganese-molybdenum-nickel alloy steel plate. | Used for the heads (domes) of pressure vessels. |
3. Manufacturing: The 15,000-Ton Requirement
Nuclear forging is a "bottleneck" technology because only a few facilities globally can handle the scale:
-
Ultra-Clean Melting: Steel is refined using Vacuum Degassing (VD) to remove hydrogen, preventing "internal flakes" that could cause a meltdown-level failure.
-
Gigantic Presses: Manufacturing a Gen III+ RPV requires a hydraulic press with a capacity of 14,000 to 15,000 tonnes.
-
Integral Forging: Modern designs prefer "integral" forgings where nozzles (entry points for water) are forged as part of the shell ring rather than being welded on later. This eliminates the "Heat Affected Zone" (HAZ) where cracks usually start.
4. Regulatory & Quality Codes
Unlike general manufacturing, "good" isn't enough; "documented perfection" is required.
-
ASME Section III (Division 1 & 5): The "Bible" of nuclear construction. It dictates everything from the chemistry of the ore to the temperature of the forge shop.
-
NQA-1: The Quality Assurance standard that requires a "Nuclear Traceability" paper trail for every single atom in the component.
-
10 CFR Part 21: A US federal regulation requiring manufacturers to report any "defect or non-compliance" that could create a substantial safety hazard.
5. Future Trends: Gen IV and SMRs
-
Small Modular Reactors (SMRs): These use smaller forgings that can be produced by a wider range of forge shops, potentially lowering costs and shortening lead times.
-
Gen IV High-Temp Materials: Next-gen reactors (Lead-cooled or Molten Salt) operate at 700°C+. This requires new forged alloys like Type 316H or Hastelloy N, which are still undergoing ASME qualification.
-
PM-HIP (Powder Metallurgy): A new process where metal powder is compressed under heat to create complex shapes, potentially replacing some traditional forgings.
FAQ: Nuclear Power Forgings
Q1: Why are there so few suppliers for nuclear forgings?
-
A: The entry barrier is massive. You need a 15,000-ton press (costing hundreds of millions), a nuclear-certified supply chain, and "Nuclear Stamps" (certifications) that take years to earn. Currently, Japan Steel Works (JSW) and a few firms in China, Russia, and France dominate the market.
Q2: What is "Neutron Embrittlement"?
-
A: Over decades, the constant bombardment of neutrons knocks atoms out of place in the forging's crystal lattice. This makes the metal brittle. Forgings are designed with specific "chemistry limits" (low Copper and Phosphorus) to slow this process down.
Q3: Can a nuclear forging be repaired once it’s in service?
-
A: It is extremely difficult due to the radioactivity of the component (the "hot" zone). Most repairs are done by underwater robots using specialized remote welding. This is why the initial forging quality must be nearly perfect.


 English
English 中文简体
中文简体