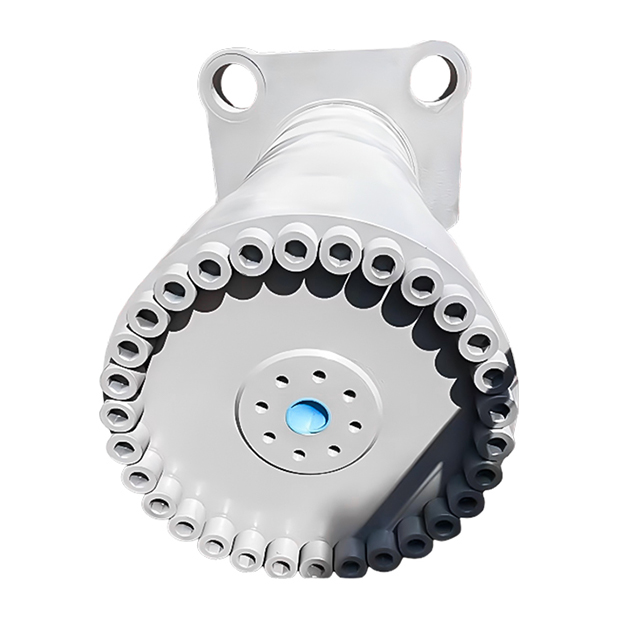
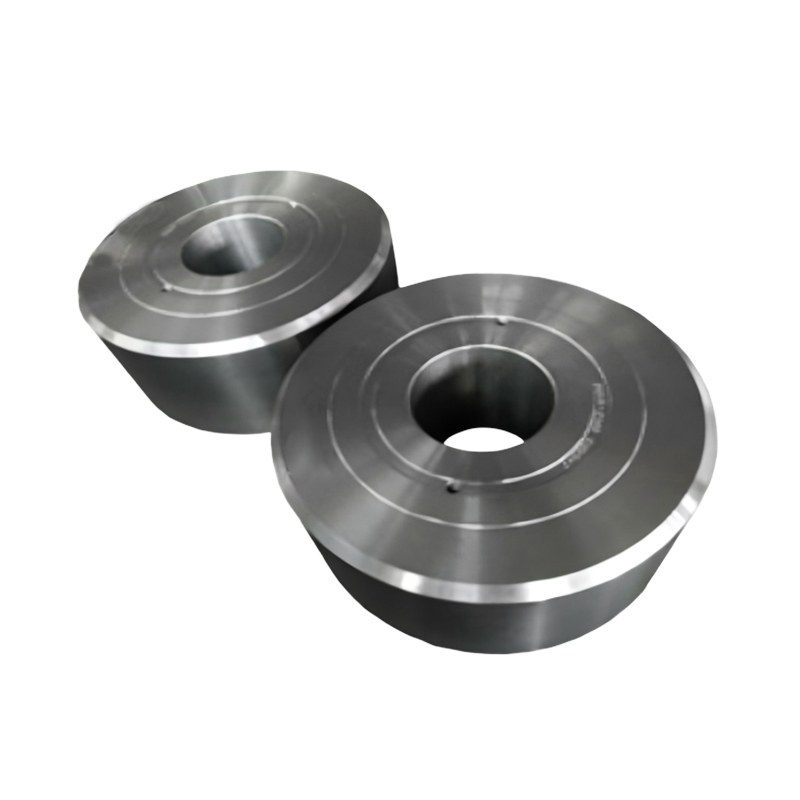
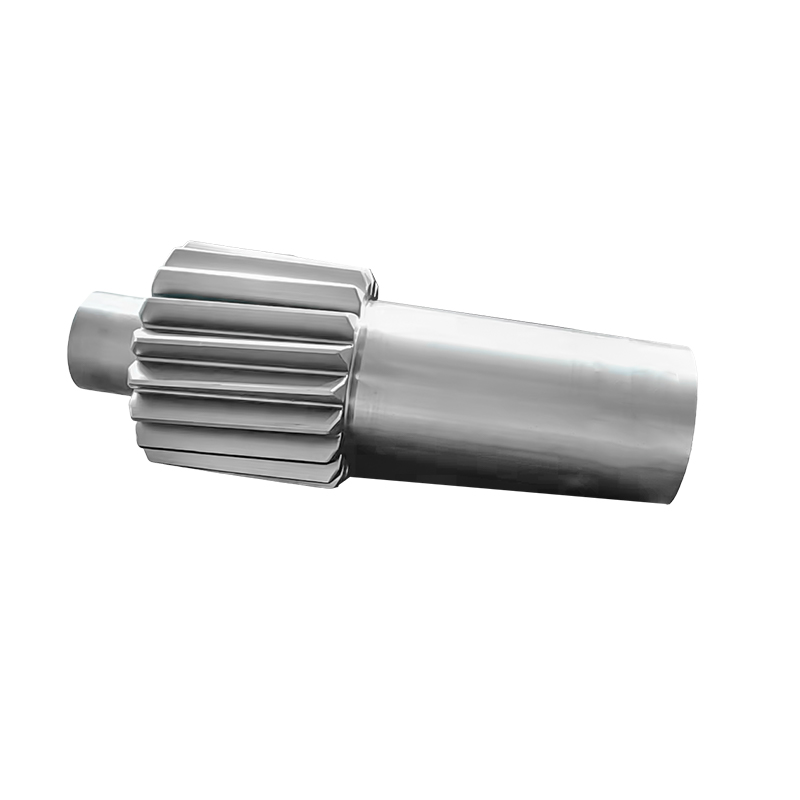
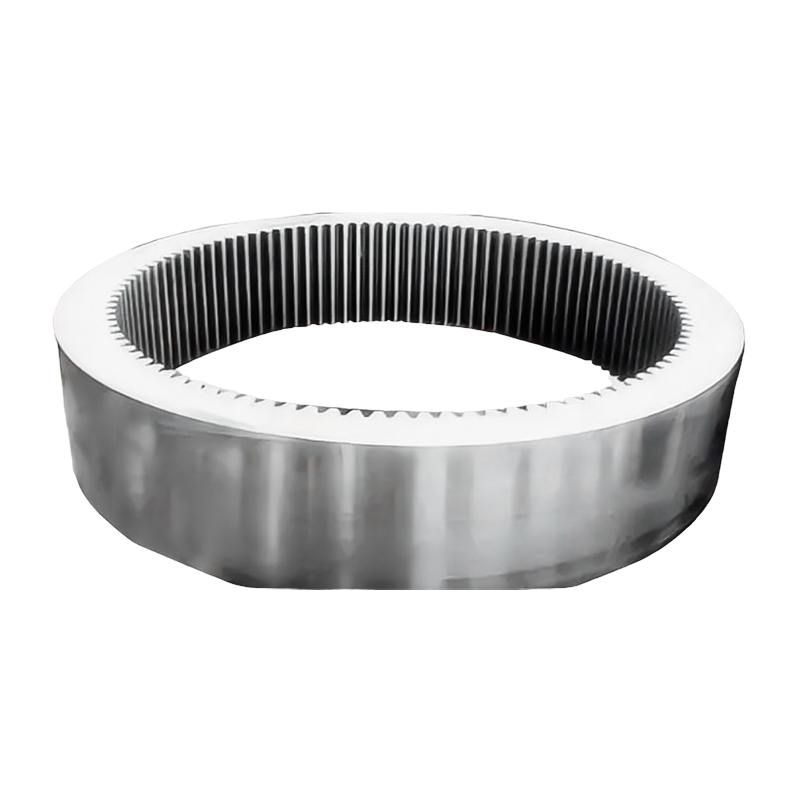
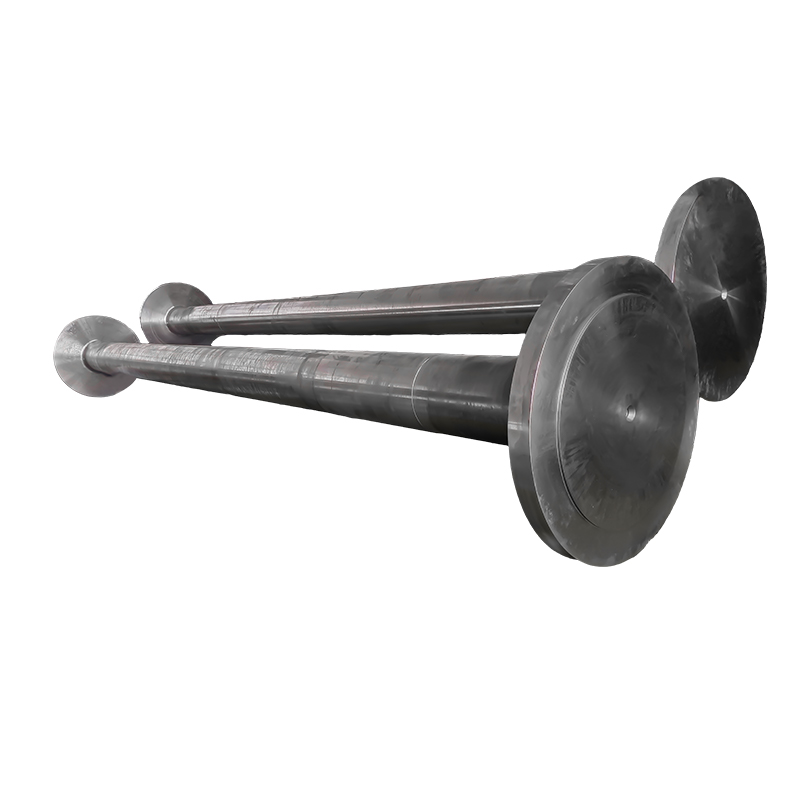
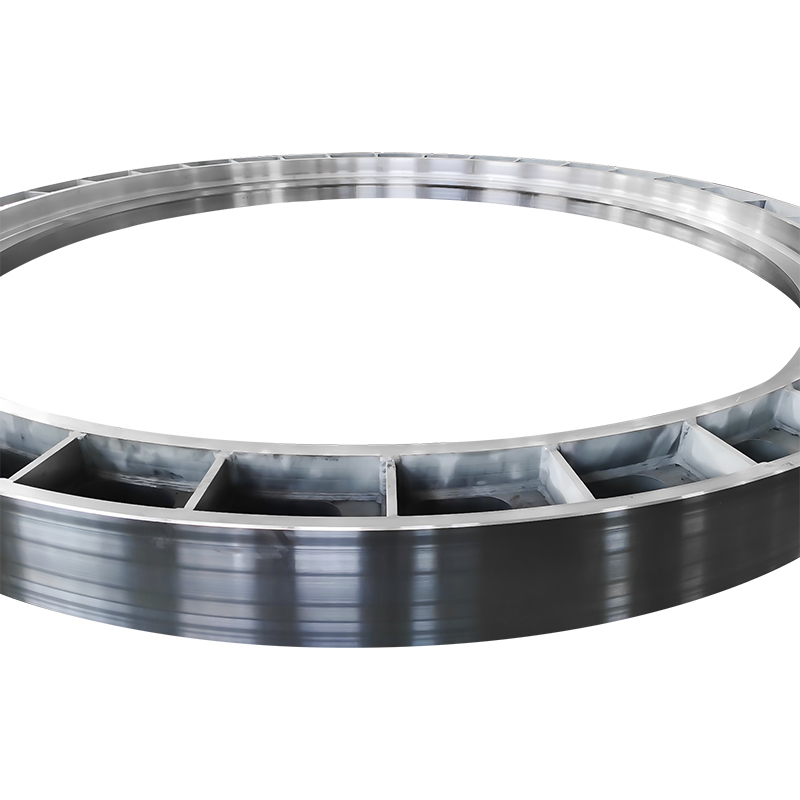
Weldment
1. Core Advantages
Flexible Sizing & Customization: Can be spliced into arbitrarily complex sizes on demand, adapting to diverse application scenarios (e.g., large-span structures, compact equipment spaces).
Versatile Material Selection: Supports flexible material options to meet multi-dimensional requirements such as high strength, corrosion resistance, and lightweight properties. Notably, the joint performance remains stable, ensuring structural integrity after assembly.
Lightweight & High Efficiency: Achieves "lightweight and high efficiency" through structural optimization (e.g., adding stiffening ribs to enhance load-bearing capacity, designing weight-reduction holes to reduce overall mass). This balance between cost and performance makes it cost-effective for large-scale applications.
2. Key Application Selling Points
These components serve as core load-bearing and functional parts across multiple industries, with standout advantages tailored to sector-specific needs:
Construction & Construction Machinery: Excels in large-span and high-strength performance, perfectly adapting to heavy-load requirements (e.g., bearing construction equipment weight) and spatial constraints (e.g., covering wide building spans).
Transportation & Aerospace: Leverages lightweight materials to reduce energy consumption—critical for improving fuel efficiency of vehicles (e.g., commercial trucks, high-speed trains) and extending the endurance of aerospace equipment (e.g., drones, aircraft components).
Chemical Industry & Medical Field: Relies on corrosion-resistant or specialized materials to withstand harsh environments. For example, in chemical plants, it resists erosion from corrosive media (e.g., acids, alkalis); in medical settings, it meets strict hygiene and biocompatibility standards (e.g., for medical device frames).


 English
English